Early diagnosis may be critical and requires a multidisciplinary team1,2
- Dermatologists may be the first to recognize the signs of this hematologic malignancy because ~90% of patients present with skin lesions1-5
- Pathologists are essential for diagnosing BPDCN, as correct diagnosis relies on a compatible immunophenotype, including the signature marker triad, CD123, CD4, and CD56, among other markers1,4,5*
- Hematologist-oncologists are key in accurately diagnosing BPDCN, differentiating it from more common cancers with similar presentations1,2,5-7
Historically, BPDCN has had poor clinical outcomes8,9
Historical overall survival8
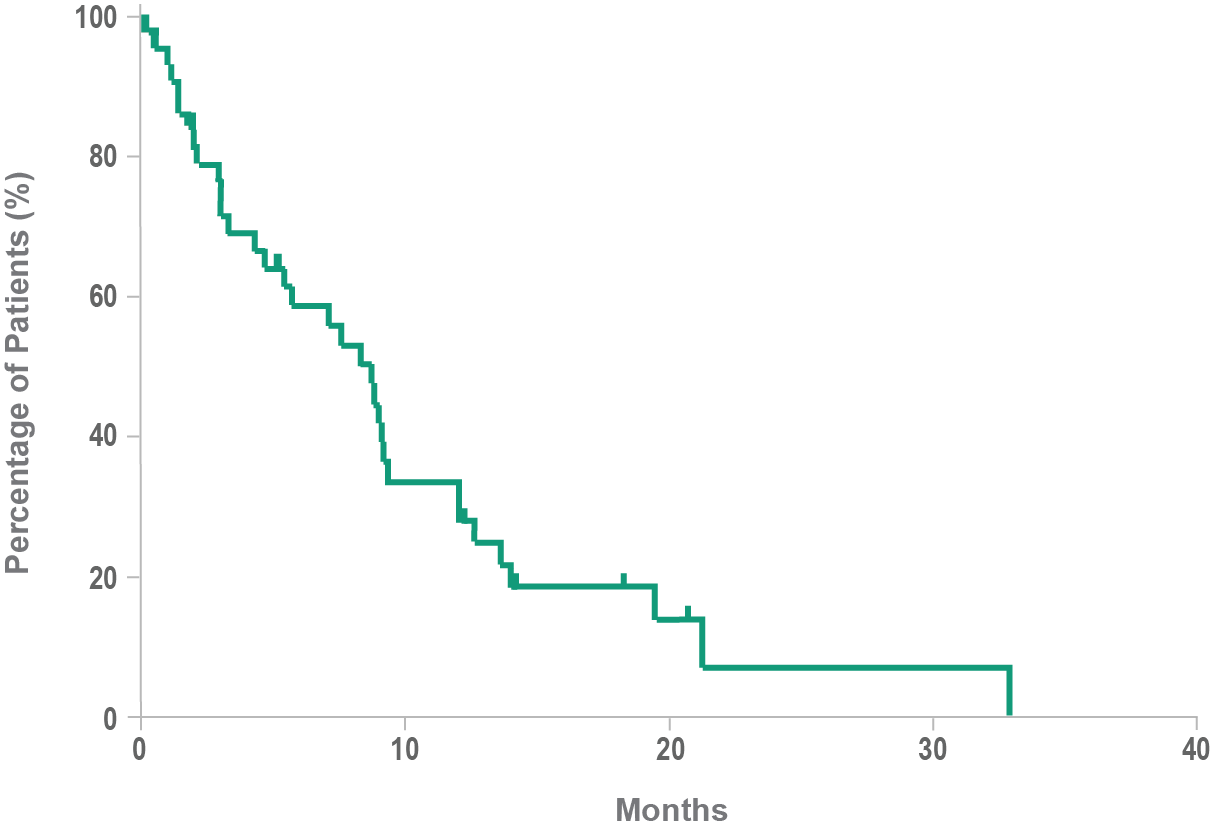
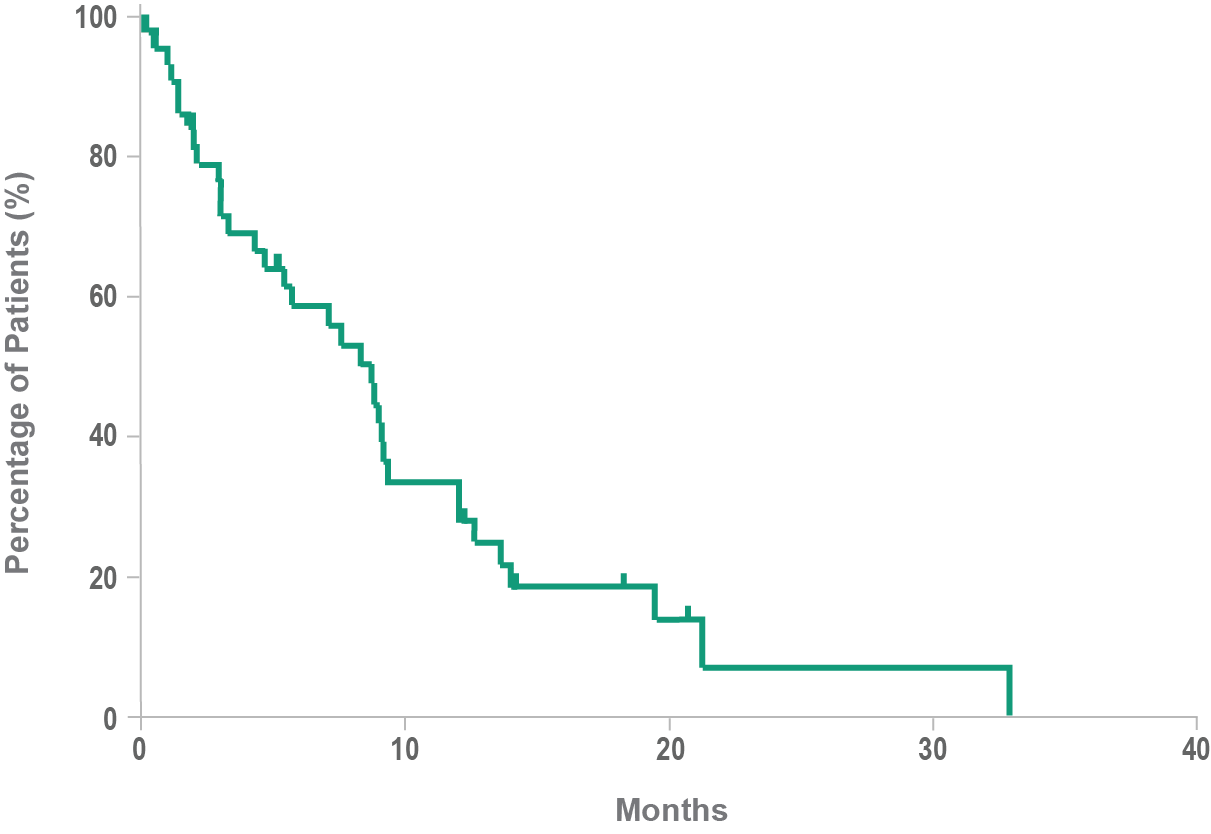
- Historically, median overall survival for BPDCN is approximately 8 to 14 months after diagnosis8,9
- In a retrospective analysis, the mean time between the onset of lesions and the final diagnosis of BPDCN was 6.2 months3
BPDCN is currently recognized as a unique myeloid neoplasm after years of reclassification
Evolving World Health Organization classification for BPDCN1,10
Blastic NK-cell lymphoma
CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm
BPDCN as a subset of AML
BPDCN as a unique myeloid neoplasm
In the most recent WHO 2022 classification, BPDCN is classified under dendritic cell and histiocytic neoplasms11
Frequent reclassification and renaming have likely contributed to the underrecognition of BPDCN1
Who are patients with BPDCN?
The exact incidence of BPDCN is unknown because the nomenclature used to describe BPDCN has evolved over the years along with an understanding of the underlying biology.1
74%
are men11
Typically diagnosed in patients'
60s or 70s,
but can develop at any age1,12
Affects all races and
geographic locations1
Have you seen a case of BPDCN?
Similarity to other hematologic malignancies may contribute to misdiagnosis.1,2,5,7,10 Approximately 10% to 20% of patients with BPDCN have a previous history of, or may have been misdiagnosed with, certain other hematologic malignancies, including MDS, CMML, and AML.1
BPDCN may be mistaken for2,5,7:
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- Leukemia cutis
- Myeloid sarcoma
- NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML)
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)
To help identify BPDCN, think CD1234561,5
- CD123, CD4, and CD56 comprise a signature marker triad that is key in diagnosing BPDCN1,8*
- CD123 can be both a diagnostic marker and a therapeutic target in BPDCN13
- BPDCN can be diagnosed through any biopsy of malignant cells12
*BPDCN diagnosis can include other markers, such as TCL1, TCF4, and CD303 (BDCA-2).1,14
Delay in the correct diagnosis can mean that by the time BPDCN is recognized, disease progression may already have occurred6
ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; BPDCN, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; NK, natural killer; WHO, World Health Organization.
- References:
- Pagano L, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: diagnostic criteria and therapeutical approaches. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(2):188-202.
- Hirner JP, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: the dermatologist's perspective. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020;34(3):501-509.
- Julia F, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: clinical features in 90 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):579-586.
- Sullivan JM, Rizzieri DA. Treatment of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016;2016(1):16-23.
- Laribi K, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: from origin of the cell to targeted therapies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(8):1357-1367.
- Riaz W, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm: update on molecular biology, diagnosis, and therapy. Cancer Control. 2014;21(4):279-289.
- Goyal A, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. In: Carter JB, et al, eds. Atlas of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Classification and Differential Diagnosis. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing Switzerland; 2015:193-203.
- Pagano L, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study. Haematologica. 2013;98(2):239-246.
- Pemmaraju N. Novel pathways and potential therapeutic strategies for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN): CD123 and beyond. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017;12(6):510-512.
- Arber DA, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127(20):2391-2405.
- Jain A, et al. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2023;21(5):515-521.
- Facchetti F, et al. Neoplasms derived from plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Mod Pathol. 2016;29(2):98-111.
- Frankel AE, et al. Activity of SL-401, a targeted therapy directed to interleukin-3 receptor, in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients. Blood. 2014;124(3):385-392.
- Ceribelli M, et al. A druggable TCF4- and BRD4-dependent transcriptional network sustains malignancy in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. Cancer Cell. 2016;30(5):764-778.